Sublimation vs screen printing are two separate technologies that offer different things in terms of print quality, colour gamut, print compatibility, setup and production time, environmental effect, and adaptability.
Sublimation and screen printing are two of the most used printing techniques for creating personalized prints, such as t-shirts, mugs, and other items.
Both provide effective and reasonably priced methods for producing individualized print goods, but their approaches differ somewhat. For bright, long-lasting effects, sublimation printing uses heat to directly infuse sublimation inks into coated surfaces.

Stenciled screens are used in screen printing to transfer ink onto surfaces. Screen printing is superior for low-cost, large-volume bulk orders of simpler patterns, while sublimation works best for full-color graphics such as photorealistic images.
If you’re starting a custom printing project, you should consider whether dye-sublimation or traditional screen printing would better serve your needs in terms of quality, customization options, suitable formats, and cost structures.
When choosing between sublimation and screening procedures, retailers should consider the main advantages and disadvantages as outlined in this comparison.
Get to know what kind of printer do you need for sublimation printing and how to print sublimation images?
What is Sublimation Printing?
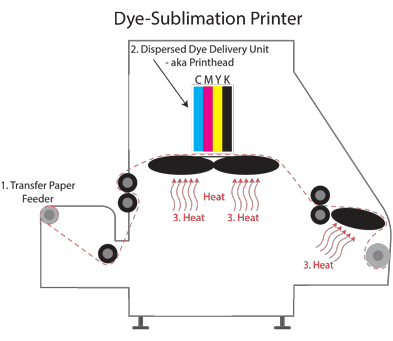
Sublimation printing is a digital process that transfers dye onto materials using heat and pressure. The image is first printed onto sublimation paper with specialized inks in this procedure.
After that, the paper is put to the substrate, and the heat causes the ink to sublimate, bonding with the substance.
Sublimation is well-known for reproducing detailed and full-color graphics, making it suited for polyester textiles and materials with a polymer coating.
As the ink becomes a part of the material, the procedure produces a soft and smooth surface with a comforting feel.
Sublimation printing is useful for short production runs and has environmental advantages because it often uses water-based inks.
Sublimation Printing Tutorials
What is Screen Printing?
Screen printing, on the other hand, is a conventional technique that involves forcing ink through a mesh screen onto the substrate.
Each colour in the pattern requires its own stencil (screen), and the final image is created by forcing ink through the open sections of the screen.
Screen printing works best with solid colors and bold designs, but it struggles with tiny details and colour gradients.
It is adaptable to a wide range of materials, including cotton, polyester, and mixes. Screen printing frequently results in a thicker coating of ink on the surface, resulting in a slightly elevated and more visible print.
Sublimation Printer Pricing analysis
Screen printing takes longer to set up since different screens must be created for each colour, but it is more efficient for big production runs of the same design. However, the environmental impact may be greater because solvent-based inks may be used.
Finally, the choice between sublimation and screen printing is determined by project needs such as material type, design complexity, desired print feel, and manufacturing scale. Each approach has advantages for different uses in the printing business.
How To Sublimate on Polyester Fabrics?
Why is my sublimation printer printing lines?
Fundamentals of Sublimation & Screen Printing

Sublimation is a type of digital printing that uses the sublimation process. Using specialized inks, a picture is initially printed onto sublimation paper in this technique. The sublimation paper is then put to the substrate, and the image is transferred using heat and pressure.
The dye turns into a gas and binds with the material during this process, resulting in bright, full-color prints.
Dye sublimation works especially well with polyester textiles and materials with a polymer coating. Because the ink becomes an inherent part of the cloth, the prints have a soft and smooth feel.
Screen printing, on the other hand, is a more conventional method that includes passing ink through a mesh screen onto the substrate.
Each colour in the pattern requires its own stencil or screen, and the final image is created by forcing ink through the open sections of the screen.
Screen printing is well-known for providing solid colors and striking graphics. It may, however, encounter difficulties when working with fine features and colour gradients.
The method is adaptable to a wide range of materials, including cotton, polyester, and mixes. Screen printing leaves a thicker coating of ink on the surface, giving the product a distinct tactile sensation.
When it comes to colour complexity, dye sublimation stands out because to its ability to print complicated and full-color graphics, making it ideal for applications requiring precise details.
Ghosting issue solution available
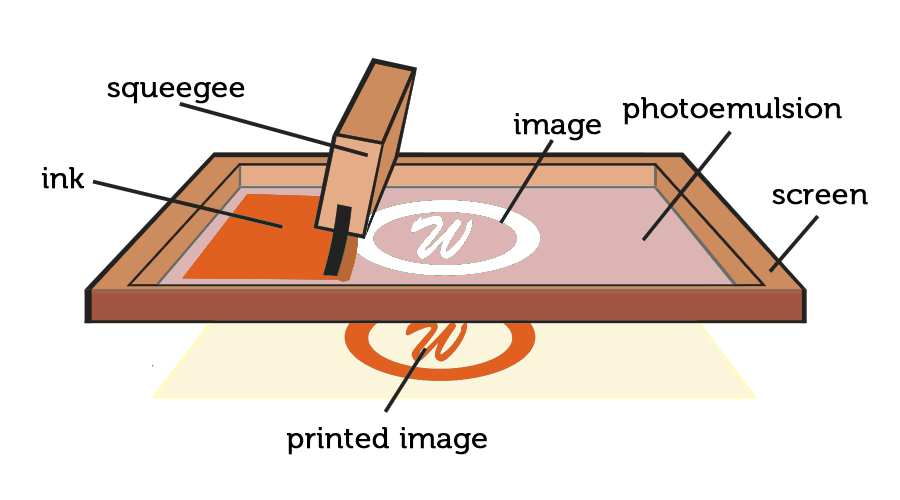
Screen printing, on the other hand, is used for simpler, bolder graphics with less colour changes. The decision between these technologies is frequently influenced by considerations such as material type, design complexity, desired tactile feel, and production scale.
Each process has advantages and disadvantages and is chosen depending on unique project requirements in the printing business.
15 Key Differences: Sublimation Vs Screen Printing
1) Ink application:
Sublimation printing involves infusing ink into the fabric or substrate, effectively coloring the material at the molecular level. This permits the ink to become part of the substrate rather than just sitting on top of it. Screen printing involves applying ink to the material’s surface. Instead of integrating into the substance, the ink cures and adheres to it.
2) Ink Durability:
Because the sublimation dye is incorporated into the substrate, the prints are exceptionally durable and permanent. They will not crack, fade, or peel away from the material over time. Screen printed ink has reduced durability since it lies on the surface and can break, split, or peel away from the material due to wear or washing.
3) Color Range:
Sublimation printing may produce up to 16 million colors by combining cyan, magenta, yellow, and black dye panels. This enables near-photographic image replication. Screen printing also uses CMYK colored inks, which mix to create a wide range of colors, although the color gamut is less, often approximately 10,000 colors.
4) Photorealistic output:
The ability to print continuous tones in millions of hues enables sublimation to produce true photorealistic prints. The visuals will be bright and vivid, with seamless color changes. Screen printed graphics have a rasterized, dot matrix pattern created by the ink and mesh screens. This results in an identifiable dotted look rather than a clear photographic image.
5) Ideal Textiles:
Polyester and polymer-coated synthetics are the best fabrics for sublimation because the ink can bond with the coating. Natural materials, such as cotton and canvas, lack this coating, thus sublimation does not operate on them. Screen printing can accept a larger range of textiles, including natural fabrics that sublimation cannot properly print on.
6) Hard Surface Printing:
Sublimation allows you to print directly onto hard surfaces such as ceramics, metals, wood, and other things having a polyester coating. The print melts with the coated surface. Traditional screen printing ink does not bond well with these hard items and requires a substrate such as paper.
7) Set-up Time:
Because it uses a digital file workflow, sublimation printing is quick and simple to set up for large production runs. Screen printing requires further preparation, such as emulsion coating and curing screens, before production can begin. This additional setup makes screen printing less suitable for small print runs.
8) Print runs:
The automated sublimation method reduces costs for greater volume manufacturing runs by spreading setup time across more items. Screen printing is better suited to smaller batches due to its cheaper setup costs. Screen printing reduces per-unit production costs in small numbers.
9) Customization:
Screen printing offers greater customisation by allowing for multi-layered prints, the use of unique inks, and the creation of effects such as puffed ink. The sublimation technique has less options for these kind of specific printing adaptations.
10) Registration:
Sublimation printing allows for highly exact color alignment during the printing process. The color-to-color registration produces sharp images and graphics. Screen printing’s manual alignment makes registration less accurate and can cause blurring.
11) Environmental Impact:
Sublimation, as a digital process, produces no chemical waste or byproducts associated with screen printing screen setup. Screen printing makes use of solvents and chemicals to prepare screens, which must then be washed and disposed.
12) Location Flexibility:
Screen printing only requires a screen setup and may be done practically anywhere, indoors or outdoors. Sublimation is dependent on heat presses and equipment, which may have additional electrical and power requirements, as well as space requirements.
13) Equipment Costs:
Screen printing supplies, such as screens and squeegees, offer a cheaper starting cost than sublimation heat presses and specialty ink printers. However, high-volume sublimation equipment has better efficiency and automation possibilities.
14) Operator Skill:
A qualified screen printing professional is essential for achieving high-quality outcomes. The automated sublimation technique is essentially a skill-free digital printing procedure.
15) Profit margins:
For smaller orders, screen printing will typically generate higher profit margins and be more profitable per unit. However, sublimation can generate larger total margins by producing large orders efficiently.
Can you sublimate on rayon fabrics?
We can use a regular printer for sublimation?
Pros and Cons of Sublimation and Screen Printing:
Sublimation printing and screen printing are two popular printing techniques, each with their own sets of pros and cons. Here is a comparison between sublimation and screen printing:
Sublimation Printing
How it Works: Sublimation printing uses heat to infuse specially-coated blank items like mugs, fabrics, metals, etc. with durable dyes. The ink transforms into a gas under heat and permanently bonds with the polymer coating on the substrate.
Pros:
- Fade-resistant and durable full-color prints integrated into the item
- Ability to print all-over prints including wraps and customization on mugs, apparel, etc.
- Exceptional reproduction of photographs and complex graphics
- No setup fee or minimum order quantity in most cases
Cons:
- Requires specially coated blank items which cost more
- Limited choice in materials able to be sublimated
Sublimation Printing is Ideal For: Full color all-over customization including fabrics, mugs/drinkware, mirrored materials, metals, wood, etc. Complex graphics like photorealism.
Screen Printing
Screen printing presses ink directly onto items through stencils and a mesh screen template for each color. Ink lays on top of the material and cures into a permanent print.
Pros:
- Very cost-effective for bulk orders and large teams/groups
- Huge variety of ink and blank apparel colors
- Can print on uncoated standard items like t-shirts, hats, posters, etc.
- Established technology with widespread access
Cons:
- Requires artwork separation for multi-color designs
- Higher setup costs for stencils and screens
- Not as vibrant or fade-resistant as dye sublimation
Screen printing is used for: Affordable custom apparel in bulk like team jerseys, corporate shirts, etc. Can be used for posters and decals on common items.
In summary, sublimation offers exceptional full-color print vibrance and durability while screen printing excels at bulk orders of standard items like apparel. Evaluate key factors like design complexity, order quantity, and materials to determine the best process.
FAQ’s:
Sublimation printing offers more photorealistic quality and more brilliant colours than screen printing. Sublimation allows for accurate photographic reproductions by printing continuous tones in millions of colour combinations. Screen printing is limited to CMYK coloured inks, hence the colour gamut is less. The ink is also applied in little dots, giving the images a lower-quality rasterized appearance.
Because the ink is infused directly into the polyester fibres, sublimation printing produces highly durable prints. Even after multiple washes and wears, the print remains brilliant and persistent. Screen printed ink lies on top of the cloth, making it susceptible to cracking, fading, and peeling over time, particularly on flexible athletic wear.
The main distinction is that sublimation printing infuses the ink into the fabric, whereas screen printing applies the ink on top of the substrate. During the heat pressing process, sublimation dyes form a molecular bond with the polyester fabric. This permits the ink to permanently adhere to the cloth. Screen printing ink dries on top of the material, forming a printed layer that adheres to the surface.
Sublimation printing has the advantage of being quick and straightforward to set up because it uses digital printer files and heat presses. Screen printing necessitates more physical preparation, such as masking screens and mixing inks for each job. This additional setup makes screen printing less suitable for printing small amounts.
Sublimation is only effective on polyester and polymer-coated synthetic materials since the ink requires a polymer coating to connect with. Natural fabric fibres, such as cotton and canvas, lack the coating, hence sublimation will not provide satisfactory results. Screen printing is suitable for a wide range of textiles, including cotton t-shirts, canvas bags, and synthetic blends. The ink adheres to the fabric surface.
Sublimation printing allows you to decorate hard items such as mugs, glasses, plaques, lamps, ceramics, metal, and more, as long as the surface is covered with a polyester polymer. Uncoated surfaces, such as cardboard, do not perform well. Screen printing requires an absorbent surface for the ink to adhere to, therefore it works best on softer materials such as paper and cardboard.
Sublimation outperforms screen printing in terms of print definition, resolution, and colour depth. The continuous-tone photorealistic prints do not have a dotted appearance like screen-printed images. Sublimation allows for extremely fine colour registration, whereas screen printing registration can be off.
When printing big quantities, sublimation printing provides significantly lower per-unit costs. The automatic setup spreads the initial costs across many products. On large batches, screen printing requires a lot of labour and is less efficient, which raises the cost per item. Screen printing is frequently more cost-effective for small batches.
To obtain high-quality prints, screen printing requires qualified professionals to set up the screens, manage squeegee pressure, and align registration. Because automated sublimation is a digital printing method, it is easier to use in its basic form. But talented graphic designers are still required.
Sublimation is a more environmentally friendly procedure that produces little waste – mostly the printed transfer paper. Screen printing involves the use of chemicals and solvents to prepare the screens. When a work is finished, the stencils must be washed with water, which generates further trash.
Sublimation Printer Settings Guide
What is Cricut Sublimation Printer?








14 Comments